How do male and female facelifts differ?
From a surgical and aesthetic point of view, facelifts in males can differ from facelifts in females in several ways:
Facial anatomy: Male and female facial structures have inherent differences. Men tend to have thicker skin, stronger facial muscles, and more pronounced bone structure compared to women. Surgeons need to take these anatomical differences into account when planning and performing facelifts for men.
Goals and outcomes: The aesthetic goals of facelifts may differ between men and women. While women often seek a more youthful and rejuvenated appearance with softer features, men typically desire a more masculine and defined look. Male facelifts aim to preserve or enhance masculine features, such as a strong jawline and a more chiseled appearance.
Incision placement: The placement of incisions may vary between male and female facelifts. In general, male facelifts tend to use incisions that follow the natural beard line to minimize visible scarring. Incisions can be made along the sideburns, in front of the ear, and behind the ear to allow for optimal access while keeping scars as inconspicuous as possible.
Facial hair considerations: Male facelifts must consider the presence of facial hair. Surgeons need to be mindful of preserving the natural beard growth pattern and avoiding disruption to hair follicles. Special techniques may be employed to minimize the risk of hair loss or changes in facial hair growth.
Tissue manipulation: Due to the differences in skin thickness and underlying facial structures, surgeons may need to adjust their techniques during the facelift procedure. Male facelifts may require more extensive dissection of tissues to achieve desired outcomes. The underlying musculature and connective tissue are often addressed to provide a stronger foundation for lifting and repositioning the skin.
Scarring and healing: Male skin tends to have a higher risk of scarring and slower healing compared to female skin. Surgeons take extra care to minimize scarring and ensure optimal wound healing in male facelifts. Post-operative scar management techniques and recommendations may differ to accommodate these considerations.
Fat grafting: In some cases, fat grafting or liposuction techniques may be used to enhance or refine facial features during a male facelift. This can be used to add volume to specific areas, such as the cheeks or chin, to create a more balanced and masculine appearance.
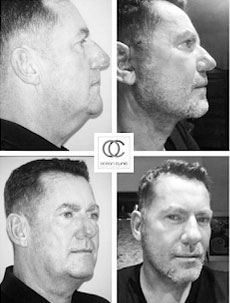
It’s important to note that these differences are generalizations, and each facelift procedure is tailored to the individual patient’s needs and goals. A skilled and experienced plastic surgeon will consider these factors while adapting the surgical approach to suit the unique characteristics of each patient, regardless of gender.
