The choice of pocket placement for breast implant insertion, i.e. where your implant will be placed, depends on factors such as the patient’s anatomy, their desired breast size and shape, their existing breast tissue, and personal preferences. All such factors would be evaluated during a consultation with your surgeon.
There are a variety of methods used when placing implants. Depending on the above, one of the following techniques will be selected to suit each patient’s individual requirements.
What is a Subglandular Breast Implant Placement
Subglandular placement refers to the implant being inserted above the muscle (between the breast tissue and the muscle - see figure 1). This method results in less post-operative tenderness but increases the risk of a less natural looking breast and rippling at the edges of the implant which can become visible. With subglandular implant placement there is also a higher risk of capsular contracture.
What is Capsular Contracture?
Capsular contracture is a complication that can occur after breast implant surgery, where scar tissue (capsule) forms around the implant and becomes thick, tight (contracts), and sometimes painful. This can cause the breast to feel hard, distorted, and uncomfortable.
Why is there a higher risk of capsular contracture with subglandular breast implants?
When breast implants are placed at a subglandular level, they are positioned between the breast tissue and the chest muscle. In this placement, the implant is in direct contact with the breast tissue, which can increase the risk of capsular contracture. The breast tissue can be more reactive to the implant, leading to the formation of a thicker and tighter scar tissue capsule.
Factors that may contribute to capsular contracture include the type of implant used, the size of the implant, the patient’s healing response, and the surgical technique used to place the implant. Capsular contracture can range from mild to severe and can occur at any time after surgery, from weeks to years later.
If capsular contracture occurs, treatment options may include massage, medication, or in severe cases, surgical removal or replacement of the implant. In some cases, changing the placement of the implant from subglandular to submuscular (under the chest muscle) may be recommended to reduce the risk of recurrence.
How high is the risk of capsular contracture in subgladnular implants?
The risk of capsular contracture in subglandular breast implants is higher compared to when the implants are placed under the chest muscle (submuscular placement). However, the exact risk can vary depending on several factors, such as how well the individual heals, the type of implant used, and the techniques applied during surgery.
Studies have reported the risk of capsular contracture in subglandular breast implants to be around 10-20%, although this can vary widely. It is important to note that capsular contracture is not predictable, and some patients may develop it even with the best surgical technique and proper care.
How can I reduce the risk of capsular contracture?
To reduce the risk of capsular contracture, surgeons may recommend various measures such as using textured implants or performing meticulous surgical techniques. As a patient, one can also take measures to reduce the risk, such as following postoperative care instructions closely, avoiding activities that can cause trauma to the breast, and attending all follow-up appointments with their surgeon.
What is a Submuscular Breast Implant Placement?
The submuscular technique was developed in order to reduce the risk of capsular contracture, to provide a more natural looking post-surgery breast, and to decrease the visibility, palpability and rippling of the implant itself. The submuscular method means that the implant is placed underneath the chest muscle.
Disadvantages involved in a submuscular breast implant placement are that the recovery period can be slightly longer, post-operative tenderness may be increased, and on occasion a “high-riding” positioning of the implant may occur within the chest pocket.
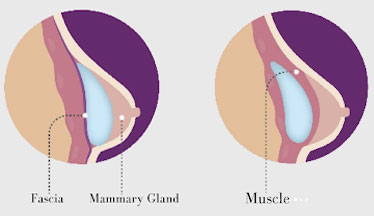
fig. 1: Submuscular breast implant location
fig. 2: Subglandular breast implant placement location
What is a Dual Plane Breast Implant Placement?
The dual plane technique is a breast augmentation surgical method in which the breast implant is placed under the pectoral muscle (upper pole of the breast) and partially under the breast tissue (lower pole of the breast). This method can help prevent constrictions of the lower pole of the breast.
In the dual plane technique, the lower edge of the pectoral muscle is released from its attachment to the chest wall, allowing the lower pole of the breast to expand and relax. The breast implant is then inserted partially under the breast tissue in the lower pole. By doing so, the implant can be better supported by the muscle and not put as much pressure on the lower pole of the breast.
This technique can help reduce the risk of implant malposition , “high-riding”, or displacement and can also result in a more natural-looking breast shape with a lower risk of constrictions in the lower pole of the breast.
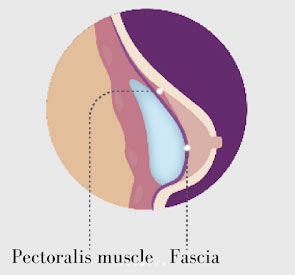
fig. 3: Dual plane implant location.
For more information on Ocean Clinic’s breast augmentation procedures please contact us today or book a consultation to discuss your options further.